Maven Authentication Guide
Adding GitHub Credentials to Maven
Purpose
This guide is intended for RetroMC developers who need to configure their local development environments to access private RetroMC artifacts published via GitHub Packages.
These credentials allow Maven to authenticate against GitHub in order to:
- Download private RetroMC dependencies
- Publish internal artifacts where required
- Build and test RetroMC projects locally without authentication errors
This setup is required for local development on projects that depend on private RetroMC packages.
Prerequisites
- A GitHub account
- Access to the relevant GitHub organisation/repositories
- Maven installed locally
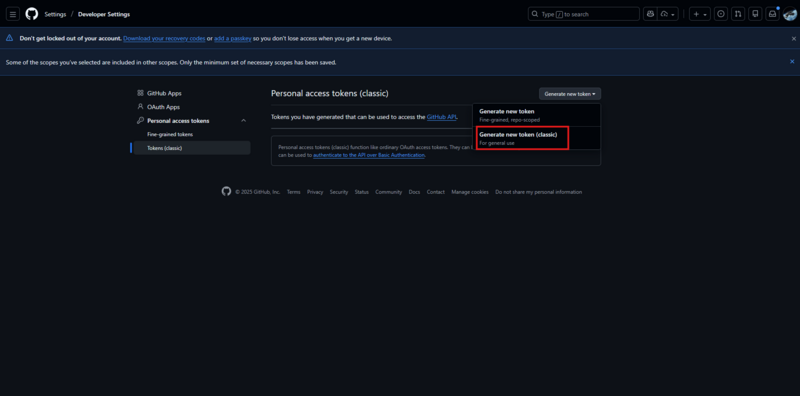
Step 1: Open GitHub Developer Settings
- Log in to GitHub
- Click your profile picture (top-right)
- Go to Settings
- Navigate to Developer settings
- Select Personal access tokens
- Click Tokens (classic)
- Click Generate new token → Generate new token (classic)
Step 2: Configure the Token
Fill in the following fields:
Token details
- Note: Use something descriptive, for example:
* Maven Main Computer
- Expiration:
* Choose a reasonable expiry date like one year (do not use No expiration under any circumstances)
Required scopes
Select only the scopes below:
repo– Required for private repositorieswrite:packagesread:packages
Leave all other scopes unchecked unless explicitly required.
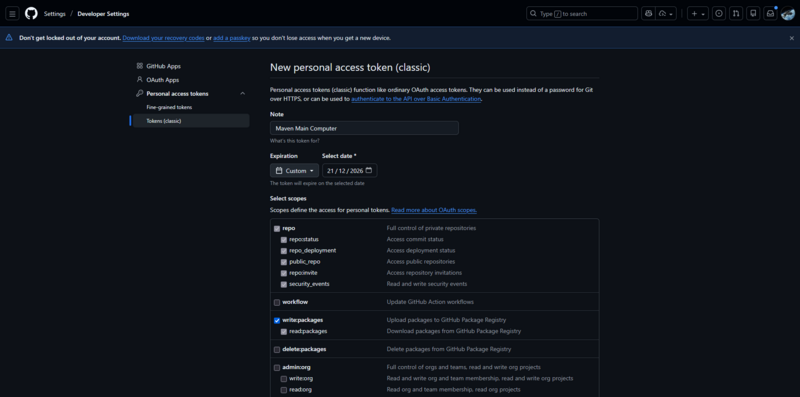
Click Generate token once complete.
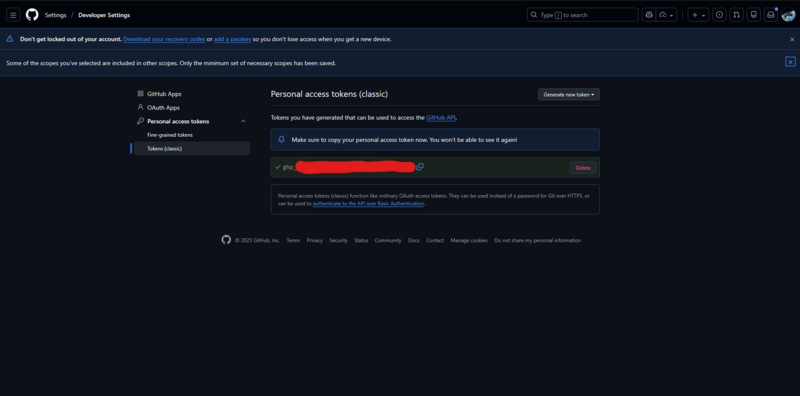
Step 3: Copy the Token (Important)
GitHub will display the token once only.
⚠️ Copy it immediately and store it securely.
If you lose the token, it must be revoked and regenerated.
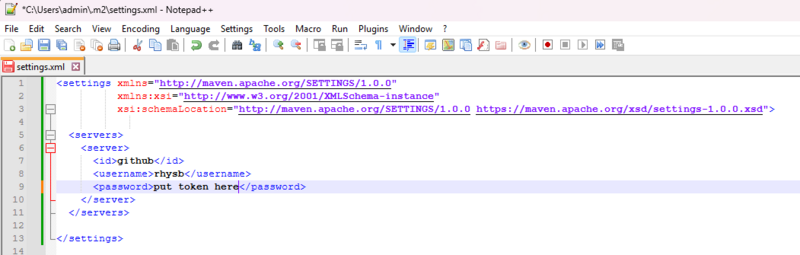
Step 4: Add the Token to Maven
Open (or create) the following file:
~/.m2/settings.xml
On Windows, this is typically:
C:\Users\<your-username>\.m2\settings.xml
Add the following configuration:
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0
https://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
<servers>
<server>
<id>github</id>
<username>YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAME</username>
<password>PASTE_TOKEN_HERE</password>
</server>
</servers>
</settings>
Replace:
YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAMEwith your GitHub usernamePASTE_TOKEN_HEREwith the generated token
Step 5: Verify
You should now be able to:
- Deploy artifacts to GitHub Packages
- Download packages from private repositories
- Run Maven builds without authentication errors
If authentication fails:
- Confirm the
<id>matches your repository id - Ensure the token includes
read:packagesandwrite:packages - Ensure you have access to the desired repository on GitHub
- Check the token has not expired
Security Notes
- Never commit
settings.xmlto Git - Do not share tokens in screenshots, logs, or chat
- Revoke tokens immediately if exposed